MTCRE Lab 1.7 - Forcing Gateways over Specific Interfaces

Introduction
In complex routing scenarios, particularly when dealing with overlapping network segments, multi-homed connections, or specific traffic engineering requirements, you may need to explicitly control which interface a router uses to reach a particular gateway. Simply specifying a gateway IP address isn't always sufficient—the router must also know which physical interface to use when forwarding packets to that gateway.
In this lab, we explore how MikroTik RouterOS handles the relationship between gateways and interfaces, and learn how to explicitly bind a gateway to a specific interface using the %interface syntax. You'll configure scenarios where the same gateway IP could theoretically be reached via multiple interfaces, and learn how to force RouterOS to use a specific path. Understanding this concept is crucial for MTCRE candidates, as it demonstrates fundamental principles of next-hop resolution, interface binding, and precise traffic control.
By the end of this lab, you'll understand when and why to bind gateways to specific interfaces, how RouterOS resolves next-hop interfaces, and how to troubleshoot routing issues related to interface selection.
Terminology Definitions
Gateway: The next-hop IP address to which packets should be forwarded to reach a destination network. The gateway must be directly reachable (on a connected subnet) or recursively resolvable through other routes.
Interface Binding: The process of explicitly associating a gateway IP address with a specific physical or logical interface, ensuring packets use that interface regardless of other potential paths.
Next-Hop Resolution: The process by which a router determines which physical interface to use when forwarding packets to a specified gateway IP address.
Scope: In RouterOS routing, scope defines the distance (in hops) at which a route can be used as a next-hop for other routes. Connected routes typically have scope=10, while static routes have scope=30.
Target Scope: The maximum scope value a route can have to be considered as a valid next-hop for reaching a gateway. Routes with scope values greater than the target-scope are not considered for next-hop resolution.
Immediate Gateway: The actual next-hop IP and interface that RouterOS has resolved for a route, displayed as immediate-gw=IP%interface in detailed route output.
Route Distance: The administrative distance or preference value assigned to a route. Routes with lower distance values are preferred. For static routes in RouterOS, the default distance is 1.
Gateway Reachability: The condition where a gateway IP address has a valid route (typically a connected or directly attached route) that allows the router to forward packets to it.
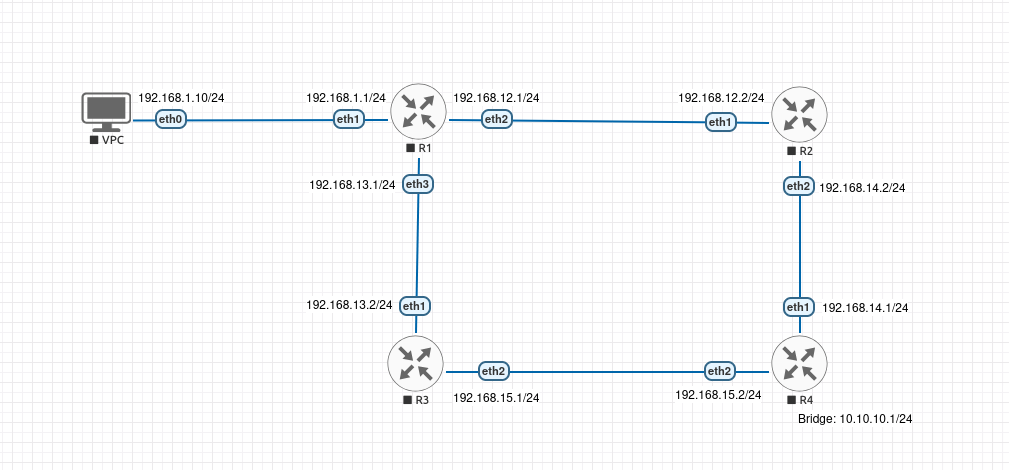
Lab Topology
Prerequisites and Starting Configuration
This lab uses the same topology as Labs 1.4 and 1.5, but requires a fresh base configuration focused on understanding interface binding.
Complete Starting Configuration
Configure VPC:
set pcname VPC1
ip 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
save
Configure R1:
/system identity set name=R1
/ip address
add address=192.168.1.1/24 interface=ether1 comment="to VPC"
add address=192.168.12.1/24 interface=ether2 comment="to R2"
add address=192.168.13.1/24 interface=ether3 comment="to R3"
# Basic route without interface specification
/ip route
add dst-address=10.10.10.0/24 gateway=192.168.12.2 comment="to R4 via R2"
Configure R2:
/system identity set name=R2
/ip address
add address=192.168.12.2/24 interface=ether1 comment="to R1"
add address=192.168.14.2/24 interface=ether2 comment="to R4"
/ip route
add dst-address=10.10.10.0/24 gateway=192.168.14.1 comment="to R4 loopback"
add dst-address=192.168.1.0/24 gateway=192.168.12.1 comment="return to VPC"
Configure R3:
/system identity set name=R3
/ip address
add address=192.168.13.2/24 interface=ether1 comment="to R1"
add address=192.168.15.1/24 interface=ether2 comment="to R4"
/ip route
add dst-address=10.10.10.0/24 gateway=192.168.15.2 comment="to R4 loopback"
add dst-address=192.168.1.0/24 gateway=192.168.13.1 comment="return to VPC"
Configure R4:
/system identity set name=R4
/ip address
add address=192.168.14.1/24 interface=ether1 comment="to R2"
add address=192.168.15.2/24 interface=ether2 comment="to R3"
# Create bridge interface for loopback simulation
/interface bridge add name=loop10 comment="Loopback 10.10.10.0/24"
/ip address add address=10.10.10.1/24 interface=loop10 comment="Destination network"
/ip route
add dst-address=192.168.1.0/24 gateway=192.168.14.2 comment="to VPC via R2"
add dst-address=192.168.12.0/24 gateway=192.168.14.2 comment="to R1-R2 link"
add dst-address=192.168.13.0/24 gateway=192.168.15.1 comment="to R1-R3 link"
Verification:
After applying the configuration, verify basic connectivity:
- From VPC, ping R4's loopback:
ping 10.10.10.1 -c 4
- On R1, check the route detail to see how the gateway is resolved:
/ip route print detail where dst-address=10.10.10.0/24
You should see immediate-gw=192.168.12.2%ether2, indicating RouterOS has automatically determined that gateway 192.168.12.2 is reachable via ether2.